
It also applies to the motion of particles within a closed system, so momentum is conserved when two objects collide. The law of conservation of momentum applies to any physical system, even those with no external force. The total final momentum is the sum of both initial and final moments. Therefore, the total initial momentum before the collision equals m1 u1 + m2 u2. During the initial and final phases of the collision, the forces applied to them equal each other. The conservation of momentum in the laws of motion states that total momentum remains constant in the absence of external forces. Newton's first law states that an object in motion will remain that way until it encounters an external force that changes its direction. However, this is not necessarily the case the seat belts work to counteract the effect of inertia. If a car crashes into a wall, the crash test dummy will fly forward.
Inertia is also the principle behind seatbelts. Objects with inertia in their state will remain motionless until they are moved by an external force. It was later incorporated into Newton's first law, which is commonly referred to as the law of inertia. The first description of inertia was made by Galileo. Inertia is the quality of a body that keeps it in the same state at rest or in motion.

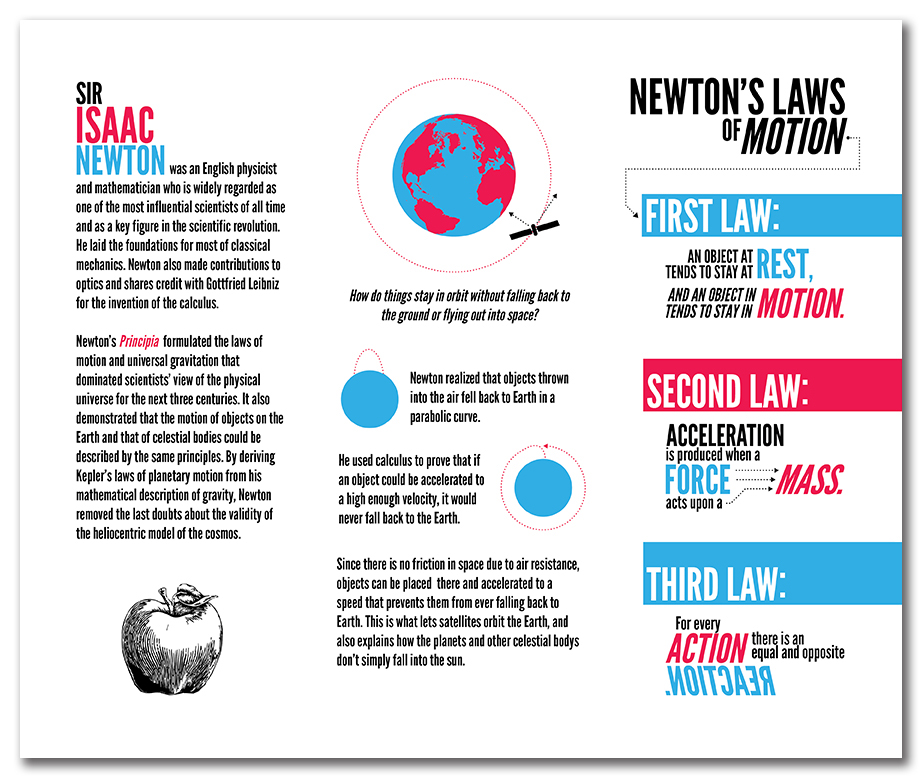
The third law states that no isolated force exists. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. The first law states that a body at rest will remain at rest unless it is acted upon by a force. They explain how the movement of matter is determined by forces and their effects on a body. Sir Isaac Newton's three laws of motion are the basis of classical mechanics. Read on to find out how you can use these laws to make your daily life easier!
If you're wondering what these three laws of motion really mean, read on! These laws are the foundation for understanding motion and the way our bodies react to the forces around us. You've probably heard of Newton's Laws of Motion, but do you know what they really mean? If not, read on! We'll cover Inertia, Conservation of Momentum, and Forces acting on an object.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
